Keyword: 線形最小二乗問題
概要
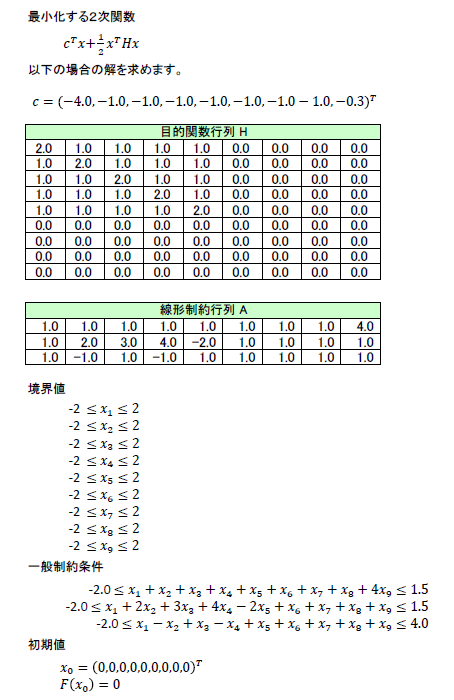
本サンプルは線形最小二乗問題を解くC言語によるサンプルプログラムです。 本サンプルは以下に示される二次関数を最小化する解を求めて、出力します。
※本サンプルはnAG Cライブラリに含まれる関数 nag_opt_lin_lsq() のExampleコードです。本サンプル及び関数の詳細情報は nag_opt_lin_lsq のマニュアルページをご参照ください。
ご相談やお問い合わせはこちらまで
入力データ
(本関数の詳細はnag_opt_lin_lsq のマニュアルページを参照)| このデータをダウンロード |
nag_opt_lin_lsq (e04ncc) Example Program Data Values of m, n, nclin 9 9 3 Objective function vector cvec -4.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -1.0 -0.1 -0.3 Objective function matrix H 2.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 2.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 2.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 Linear constraint matrix A 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 4.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 -2.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 -1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 Lower bounds -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 -2.0 Upper bounds 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 1.5 1.5 4.0 Initial estimate of x 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
- 1行目はタイトル行で読み飛ばされます。
- 3行目に目的関数行列Hの行数(m)、変数の数(n)、線形制約の数(nclin)を指定しています。
- 6行目には目的関数の係数ベクトル(cvec)を指定しています。
- 9〜17行目には目的関数行列Hの要素を指定しています。
- 20〜22行目には線形制約行列Aの要素を指定しています。
- 25行目には変数と制約の下限(bl)を指定しています。
- 28行目には変数と制約の上限(bu)を指定しています。
- 31行目にはxの初期値の推定値(x)を指定しています。
出力結果
(本関数の詳細はnag_opt_lin_lsq のマニュアルページを参照)| この出力例をダウンロード |
nag_opt_lin_lsq (e04ncc) Example Program Results Parameters to e04ncc -------------------- Linear constraints............ 3 Number of variables........... 9 Objective matrix rows......... 9 prob.................... Nag_QP2 start................... Nag_Cold ftol.................... 1.05e-08 rank_tol................ 1.05e-07 crash_tol............... 1.00e-02 hessian.................. Nag_FALSE inf_bound............... 1.00e+20 inf_step................ 1.00e+20 fmax_iter............... 60 max_iter................ 60 machine precision....... 1.11e-16 print_level......... Nag_Soln_Iter outfile................. stdout Memory allocation: state................... Nag ax...................... Nag lambda.................. Nag Rank of the objective function data matrix = 5 Itn Step Ninf Sinf/Objective Norm Gz 0 0.0e+00 0 0.000000e+00 4.5e+00 1 7.5e-01 0 -4.375000e+00 5.0e-01 2 1.0e+00 0 -4.400000e+00 0.0e+00 3 3.0e-01 0 -4.700000e+00 8.9e-01 4 1.0e+00 0 -5.100000e+00 2.3e-17 5 5.4e-01 0 -6.055714e+00 1.7e+00 6 1.1e-02 0 -6.113326e+00 1.6e+00 7 1.1e-01 0 -6.215049e+00 1.2e+00 8 1.0e+00 0 -6.538008e+00 1.6e-17 9 6.5e-01 0 -7.428704e+00 7.2e-02 10 1.0e+00 0 -7.429717e+00 3.7e-18 11 1.0e+00 0 -8.067718e+00 1.4e-17 12 1.0e+00 0 -8.067778e+00 1.4e-17 Exit from QP problem after 12 iterations. Varbl State Value Lower Bound Upper Bound Lagr Mult Residual V 1 UL 2.00000e+00 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 -8.0000e-01 0.0000e+00 V 2 FR -2.33333e-01 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.7667e+00 V 3 FR -2.66667e-01 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.7333e+00 V 4 FR -3.00000e-01 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.7000e+00 V 5 FR -1.00000e-01 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.9000e+00 V 6 UL 2.00000e+00 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 -9.0000e-01 0.0000e+00 V 7 UL 2.00000e+00 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 -9.0000e-01 0.0000e+00 V 8 FR -1.77778e+00 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 2.2222e-01 V 9 FR -4.55556e-01 -2.00000e+00 2.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 1.5444e+00 L Con State Value Lower Bound Upper Bound Lagr Mult Residual L 1 UL 1.50000e+00 -2.00000e+00 1.50000e+00 -6.6667e-02 1.3323e-15 L 2 UL 1.50000e+00 -2.00000e+00 1.50000e+00 -3.3333e-02 -8.8818e-16 L 3 FR 3.93333e+00 -2.00000e+00 4.00000e+00 0.0000e+00 6.6667e-02 Exit after 12 iterations. Optimal QP solution found. Final QP objective value = -8.0677778e+00
- 6〜7行目に線形制約の数、変数の数、目的関数の行列の行数が出力されています。
- 9〜16行目に以下に示すプログラムのオプション引数が出力されています。
prob 最小化される目的関数の種類。"Nag_QP2"は対称半正定値行列を意味します。 start 初期のワーキングセットがどのように選ばれるかを示しています。"Nag_Cold"は変数や制約の値に基づいて初期のワーキングセットが選ばれていることを意味します。 ftol 実行可能解での許容可能な制約違反の最大値。 rank_tol 三角因子の推定値を抑制します。 crash_tol 初期のワーキングセットに含まれる不等式制約が下限/上限のこの範囲内にあることを示しています。 hessian プログラムの引数hの内容を制御します。"Nag_FALSE"は引数hが変換され並べ替えられた行列HQのコレスキー因子を含むことを意味しています。 inf_bound 無限の境界値。この値以上の上限は+∞と見なされます。またこの値を負に反転させた値以下の下限は−∞と見なされます。 inf_step 無限解へのステップと見なされる変数の変化の大きさ。 fmax_iter 実行可能解生成フェーズの最大反復数。 max_iter 最適化フェーズの最大反復数。 machine precision マシンの精度。 print_level 結果出力のレベル。"Nag_Soln_Iter"は最終解と各反復の結果を出力することを意味します。 outfile 結果が出力されるファイル名。 - 18から20行目には、オプション引数state、ax、lambdaに必要なメモリがnAGライブラリの関数によって自動的に割り当てられたことを示しています。
- 22行目に目的関数行列のランクが出力されています。
- 25〜38行目には以下が出力されています。
Itn 反復回数 Step 探索方向に進んだステップ幅 Ninf 違反した制約の数 Sinf/Objective 制約違反の大きさの加重和(xが実行可能でない場合)もしくは目的関数の値(xが実行可能な場合) Norm Gz 縮小勾配のユークリッド・ノルム - 39行目にはQP問題を解くのに12回の反復が行われたことが示されています。
- 42〜51行目には以下が出力されています。
Varbl 変数を示す"V"、インデックス State 変数の状態。ULは上限であることを意味し、FRは下限も上限もワーキングセットにはないことを意味します。 Value 最後の反復での変数の値 Lower Bound 下限 Upper Bound 上限 Lagr Mult 関連する境界制約のラグランジュ乗数 Residual 残差(変数の値と近いほうの下限/上限との差) - 54〜57行目には以下が出力されています。
L Con 線形制約を示す"L"、インデックス State 制約の状態。ULは上限であることを意味し、FRは下限も上限もワーキングセットにはないことを意味します。 Value 最後の反復での制約の値 Lower Bound 下限 Upper Bound 上限 Lagr Mult 関連する境界制約のラグランジュ乗数 Residual 残差(制約の値と近いほうの下限/上限との差) - 59行目に12回の反復を行ったことが示されています。
- 61行目にQPの最適解が見つかったことが示されています。
- 63行目にQPの最終的な目的関数値が出力されています。
ソースコード
(本関数の詳細はnag_opt_lin_lsq のマニュアルページを参照)
※本サンプルソースコードはnAG数値計算ライブラリ(Windows, Linux, MAC等に対応)の関数を呼び出します。
サンプルのコンパイル及び実行方法
| このソースコードをダウンロード |
/* nag_opt_lin_lsq (e04ncc) Example Program.
*
* CLL6I261D/CLL6I261DL Version.
*
* Copyright 2017 Numerical Algorithms Group.
*
* Mark 26.1, 2017.
*
*
*/
#include <nag.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <nag_stdlib.h>
#include <nage04.h>
#define A(I, J) a[(I) *tda + J]
#define H(I, J) h[(I) *tdh + J]
int main(void)
{
Integer exit_status = 0;
Integer i, j, *kx = 0, m, n, nbnd, nclin, tda, tdh;
Nag_E04_Opt options;
double *a = 0, *bl = 0, *bu = 0, *cvec = 0, *h = 0, objf, *x = 0;
Nag_Comm comm;
NagError fail;
INIT_FAIL(fail);
printf("nag_opt_lin_lsq (e04ncc) Example Program Results\n");
fflush(stdout);
scanf(" %*[^\n]"); /* Skip heading in data file */
/* Read problem dimensions */
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
scanf("%ld%ld%ld%*[^\n]", &m, &n, &nclin);
if (m > 0 && n > 0 && nclin >= 0) {
nbnd = n + nclin;
if (!(a = nAG_ALLOC(nclin * n, double)) ||
!(bl = nAG_ALLOC(nbnd, double)) ||
!(bu = nAG_ALLOC(nbnd, double)) ||
!(cvec = nAG_ALLOC(n, double)) ||
!(h = nAG_ALLOC(m * n, double)) ||
!(x = nAG_ALLOC(n, double)) || !(kx = nAG_ALLOC(n, Integer)))
{
printf("Allocation failure\n");
exit_status = -1;
goto END;
}
tda = n;
tdh = n;
}
else {
printf("Invalid m or n or nclin.\n");
exit_status = 1;
return exit_status;
}
/* We solve a QP2 type problem in this example */
/* Read cvec, h, a, bl, bu and x from data file */
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i)
scanf("%lf", &cvec[i]);
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
for (i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
scanf("%lf", &H(i, j));
if (nclin > 0) {
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
for (i = 0; i < nclin; ++i)
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j)
scanf("%lf", &A(i, j));
}
/* Read lower bounds */
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
for (i = 0; i < nbnd; ++i)
scanf("%lf", &bl[i]);
/* Read upper bounds */
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
for (i = 0; i < nbnd; ++i)
scanf("%lf", &bu[i]);
/* Read the initial point x */
scanf(" %*[^\n]");
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf("%lf", &x[i]);
/* Change the problem type */
/* nag_opt_init (e04xxc).
* Initialization function for option setting
*/
nag_opt_init(&options);
options.prob = Nag_QP2;
/* nag_opt_lin_lsq (e04ncc), see above. */
nag_opt_lin_lsq(m, n, nclin, a, tda, bl, bu, cvec, (double *) 0,
h, tdh, kx, x, &objf, &options, &comm, &fail);
if (fail.code != NE_NOERROR) {
printf("Error from nag_opt_lin_lsq (e04ncc).\n%s\n", fail.message);
exit_status = 1;
}
/* Free options memory */
/* nag_opt_free (e04xzc).
* Memory freeing function for use with option setting
*/
nag_opt_free(&options, "all", &fail);
if (fail.code != NE_NOERROR) {
printf("Error from nag_opt_free (e04xzc).\n%s\n", fail.message);
exit_status = 1;
goto END;
}
END:
nAG_FREE(a);
nAG_FREE(bl);
nAG_FREE(bu);
nAG_FREE(cvec);
nAG_FREE(h);
nAG_FREE(x);
nAG_FREE(kx);
return exit_status;
}
