Keyword: シンプレックス法, 関数の最小化
概要
本サンプルはシンプレックス法による関数の最小化を行うC#によるサンプルプログラムです。 本サンプルはNelder-Meadシンプレックス法により以下に示される関数の最小値を求めて出力します。本サンプルではx1とx2の初期値を(−1.0,1.0)として計算しています。
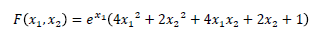
※本サンプルはnAG Library for .NETに含まれる関数 e04cb() のExampleコードです。本サンプル及び関数の詳細情報は e04cb のマニュアルページをご参照ください。
ご相談やお問い合わせはこちらまで
出力結果
(本関数の詳細はe04cb のマニュアルページを参照)| この出力例をダウンロード |
e04cb Example Program Results On exit from e04cb, ifail = 0 The final function value is 0.0000 at the point 0.5000 -0.9999
- 3行目には本関数の呼び出しでエラーが検出されなかったことを示す"0"が出力されています。
- 4行目に最小の関数値が出力されています。
- 5行目に最小の関数値に対応するxの値が出力されています。
ソースコード
(本関数の詳細はe04cb のマニュアルページを参照)
※本サンプルソースコードは .NET環境用の科学技術・統計計算ライブラリである「nAG Library for .NET」の関数を呼び出します。
サンプルのコンパイル及び実行方法
| このソースコードをダウンロード |
// e04cb Example Program Text
// C# version, nAG Copyright 2008
using System;
using NagLibrary;
using System.IO;
namespace NagDotNetExamples
{
public class E04CBE
{
static int[] iuser = new int[1];
static void Main(String[] args)
{
StartExample();
}
public static void StartExample()
{
E04.E04CB_FUNCT functE04CB = new E04.E04CB_FUNCT(funct);
E04.E04CB_MONIT monitE04CB = new E04.E04CB_MONIT(monit);
double f, tolf = 0.0, tolx = 0.0; int i, ifail, maxcal = 0;
int n = 2;
double[] x = new double[n];
Console.WriteLine("e04cb Example Program Results");
// set iuser[0] to 1 to obtain monitoring information **
iuser[0] = 0;
x[0] = -1.00e0;
x[1] = 1.00e0;
tolf = Math.Sqrt(X02.x02aj());
tolx = Math.Sqrt(tolf);
maxcal = 100;
//
try
{
E04.e04cb(n, x, out f, tolf, tolx, functE04CB, monitE04CB, maxcal, out ifail);
//
Console.WriteLine("");
if (ifail >= 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(" On exit from e04cb, ifail = {0,4}", ifail);
//
if (ifail == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(" The final function value is{0,12:f4}", f);
Console.Write(" at the point ");
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
Console.Write(" " + " {0, 12:f4}", x[i - 1]);
}
Console.WriteLine(" ");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(" {0}{1,5}", ifail);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Exception Raised");
}
}
//
public static void funct(int n, double[] xc, out double fc)
{
//
fc = Math.Exp(xc[0]) * (4.00e0 * xc[0] * (xc[0] + xc[1]) + 2.00e0 * xc[1] * (xc[1] + 1.00e0) + 1.00e0);
//
}
//
public static void monit(double fmin, double fmax, double[,] sim, int n, int ncall,
double serror, double vratio) { if (iuser[0] != 0) { int i, j;
Console.WriteLine("");
Console.WriteLine(" There have been{0,5} function calls", ncall);
Console.WriteLine(" The smallest function value is{0,10:f4}", fmin);
Console.WriteLine(" The simplex is");
for (i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
Console.Write(" {0}", sim[i - 1, j - 1]);
}
Console.WriteLine(" ");
}
Console.WriteLine(" ");
Console.WriteLine(" The standard deviation in function values at the vertices of the simplex is{0,10:f4}", serror);
Console.WriteLine(" The linearized volume ratio of the current simplex to the starting one is{0,10:f4}", vratio);
}
}
}
}
